
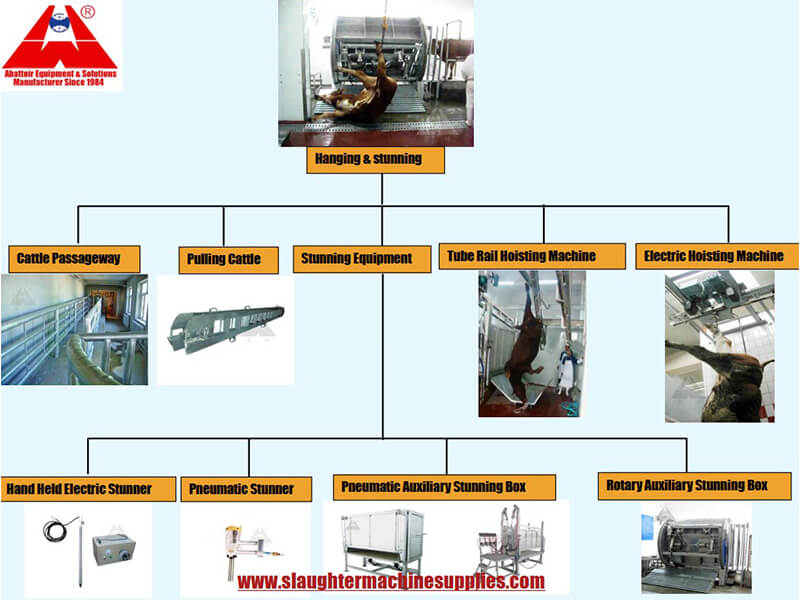
The first step in the modern abattoir slaughter line process is stunning. Stunning is a humane practice designed to render the animal unconscious before the subsequent steps of slaughter. Various methods of stunning are employed, such as captive bolt guns, electrical stunning, or gas stunning, all aimed at ensuring a quick and painless transition for the animal.

2. Bleeding
Once the animal is stunned, the next stage is bleeding. This step involves the precise cutting of major blood vessels to allow for the complete and efficient draining of blood from the carcass. Proper bleeding is crucial for both religious requirements and meat quality, as it helps prevent blood retention and ensures hygienic practices.

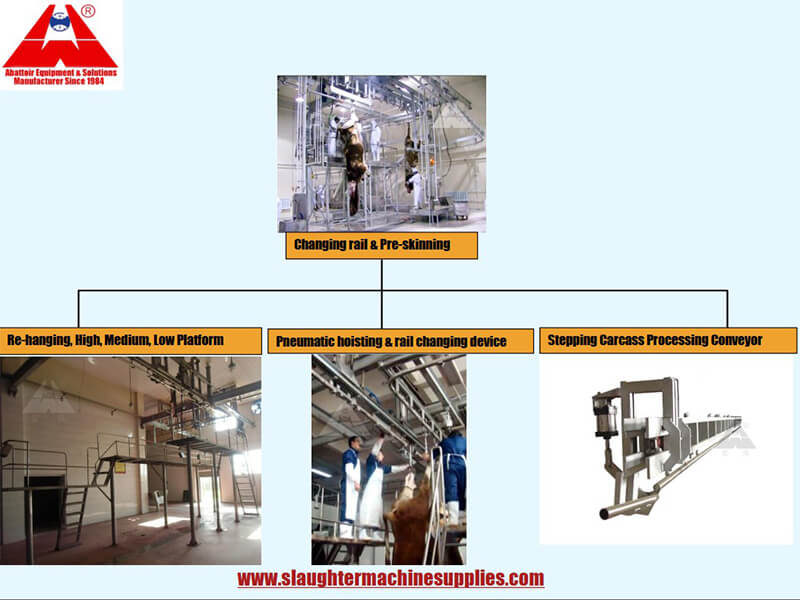
After bleeding, the carcass is transferred to the carcass processing line. This automated conveyor system is designed to transport the carcass through various stations for further processing. The line is strategically designed to optimize efficiency and minimize handling, reducing the risk of contamination and ensuring smooth workflow.

At the evisceration station, skilled workers perform the removal of the animal’s internal organs, commonly known as evisceration. This includes removing the digestive tract, reproductive organs, and other offal. Advanced tools and equipment are employed to ensure precision and efficiency in this crucial stage of the process.

5. Carcass Splitting and Chilling:
Following evisceration, the carcass is typically split into halves along the spinal column. This allows for easier handling and further processing. The carcass halves are then subjected to a chilling process to lower their temperature rapidly, ensuring food safety and preservation


6. Carcass Inspection
Throughout the entire slaughter line process, rigorous inspection protocols are in place to guarantee food safety and adherence to quality standards. Trained inspectors carefully examine the carcasses to identify any abnormalities, diseases, or contamination. This step plays a vital role in safeguarding the health of consumers.
After inspection, the carcass moves to the further processing stage, where it is transformed into various cuts and products. Skilled butchers utilize precise techniques and tools to divide the carcass into primal cuts, subprimal cuts, and retail-ready portions. This stage caters to diverse consumer demands and market requirements.

